springboot整合mybatis
1、创建普通springboot项目
2、引入依赖
3、创建实体类
4、创建3层结构
5、调用接口
1、创建普通springboot项目
用springboot的启动器创建,组件勾选spring-web组件
2、引入依赖
还需要映入3个依赖,分别是mybatis的springboot启动器,mysql的驱动,和lombok方便创建实体类。
<dependencies>
<!-- mysql驱动依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- mybatis启动器依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.26</version>
</dependency>
<!-- springboot启动器依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>3、创建实体类
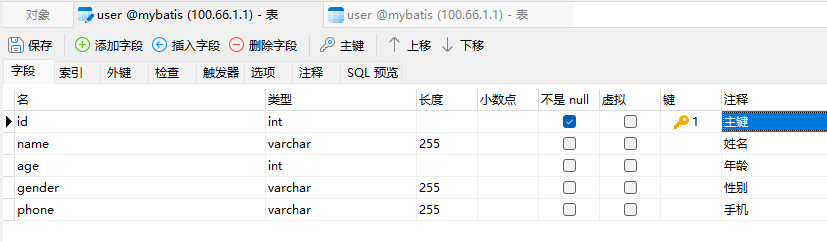
注意和数据库的保持一致

实体类:
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String gender;
private String phone;
}4、创建3层结构
分别创建mapper,service,controller.
先创建mapper:springboot-mybatis/src/main/java/com/hm/springbootmybatis/mapper/UserMapper.java
import com.hm.springbootmybatis.pojo.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user where id = #{id}")
public User getUserById(Integer id);
}在创建service和他的实现
springboot-mybatis/src/main/java/com/hm/springbootmybatis/service/UserService.java
import com.hm.springbootmybatis.pojo.User;
public interface UserService {
public User getUserById(Integer id);
}springboot-mybatis/src/main/java/com/hm/springbootmybatis/service/impl/UserServiceImpl.java
import com.hm.springbootmybatis.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.hm.springbootmybatis.pojo.User;
import com.hm.springbootmybatis.service.UserService;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public User getUserById(Integer id) {
return userMapper.getUserById(id);
}
}再创建controller:springboot-mybatis/src/main/java/com/hm/springbootmybatis/controller/UserController.java
import com.hm.springbootmybatis.pojo.User;
import com.hm.springbootmybatis.service.UserService;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Resource
private UserService userService;
/**
* 根据用户ID获取用户信息
*
* @param id 用户ID,用于查询特定用户信息
* @return 返回用户对象,如果找不到则返回null
*/
@RequestMapping("/getUserById")
public User getUserById(Integer id)
{
// 打印查询的用户ID,用于调试和日志记录
System.out.println("id:"+id);
// 调用用户服务中的获取用户方法,传入用户ID
// 这里依赖于userService,具体的业务逻辑在服务层实现
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello()
{
System.out.println("hello world");
return "hello world";
}
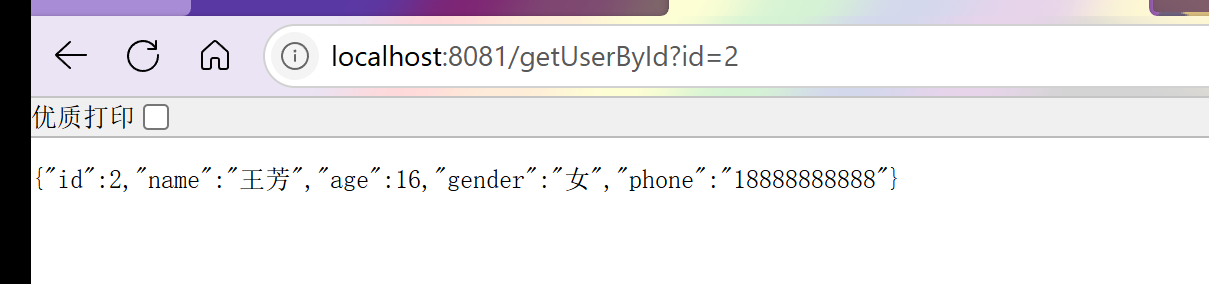
}5、调用接口
测试接口调用情况
本文是原创文章,采用 CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 协议,完整转载请注明来自 山山
评论
匿名评论
隐私政策
你无需删除空行,直接评论以获取最佳展示效果

